Molecule of the Month: H5 Hemagglutinin
Sugar-binding protein on the surface of the H5N1 avian influenza virus
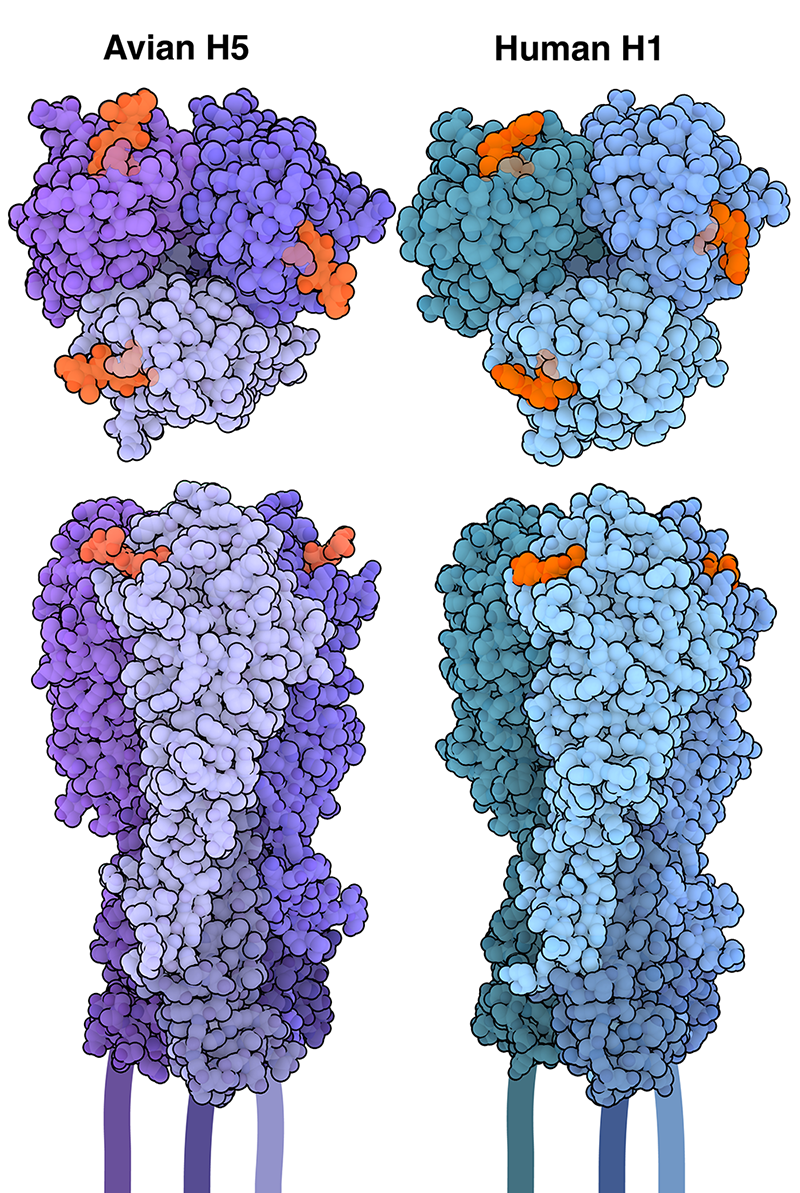
An Assortment of Subtypes
Sugar Specificity
Crossing the Species Barrier
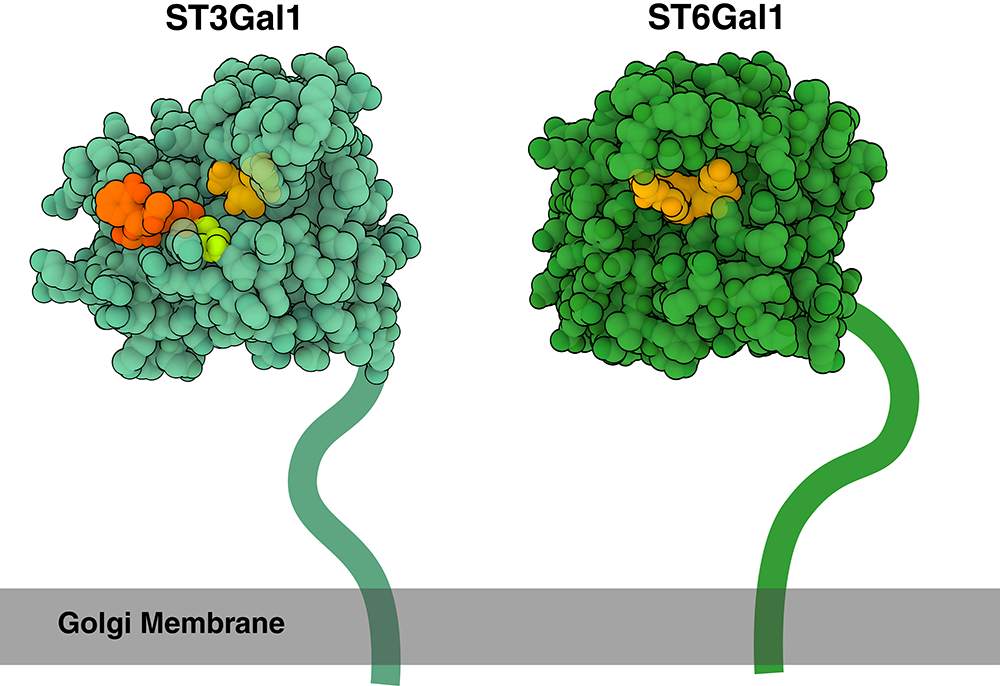
Creating a Sugar-Coated Cell
Exploring the Structure
Host Jumping
Research has shown that a change in a single amino acid can result in H5 preferentially binding to human/mammalian (α-2,6 linked) receptors rather than avian (α-2,3-linked) receptors. Specifically, changing residue 226, which is normally a glutamine, to a leucine provides a more hydrophobic environment that favors binding to mammalian receptors. Take a look at the JSmol tab to compare how H5 (PDB IDs 4K63 and 4K64) and mutant H5 (PDB IDs 4K66 and 4K67) bind to avian and human receptors.
Topics for Further Discussion
- After recognizing and binding to receptors on the cell surface, hemagglutinin attacks cells through several steps. Read more about it here.
- Learn about other components of influenza, and what a cross-section of a virus looks like here.
- Take a look at what an influenza vaccine looks like here.
Related PDB-101 Resources
- Browse Viruses
- Browse Infectious Disease
References
- 1JSN: Ha Y, Stevens DJ, Skehel JJ, Wiley DC. (2001) X-ray structures of H5 avian and H9 swine influenza virus hemagglutinins bound to avian and human receptor analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Sep 25;98(20):11181-6..
- 1RVT: Gamblin SJ, Haire LF, Russell RJ, Stevens DJ, Xiao B, Ha Y, Vasisht N, Steinhauer DA, Daniels RS, Elliot A, Wiley DC, Skehel JJ. (2004) The structure and receptor binding properties of the 1918 influenza hemagglutinin. Science. Mar 19;303(5665):1838-42.
- 2WNF: Rao FV, Rich JR, Rakić B, Buddai S, Schwartz MF, Johnson K, Bowe C, Wakarchuk WW, Defrees S, Withers SG, Strynadka NC. (2009) Structural insight into mammalian sialyltransferases. Nat Struct Mol Biol. Nov;16(11):1186-8.
- 6QVT: Harrus D, Harduin-Lepers A, Glumoff T. (2020) Unliganded and CMP-Neu5Ac bound structures of human α-2,6-sialyltransferase ST6Gal I at high resolution. J Struct Biol. Nov 1;212(2):107628.
- 4K63, 4K64, 4K66, 4K67: Zhang W, Shi Y, Lu X, Shu Y, Qi J, Gao GF. (2013) An airborne transmissible avian influenza H5 hemagglutinin seen at the atomic level. Science. 2013 Jun 21;340(6139):1463-7.
- Mair CM, Ludwig K, Herrmann A, Sieben C. (2013) Receptor binding and pH stability - how influenza A virus hemagglutinin affects host-specific virus infection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Apr;1838(4):1153-68.
- Caserta LC, Frye EA, Butt SL, Laverack M, Nooruzzaman M, Covaleda LM, Thompson AC, Koscielny MP, Cronk B, Johnson A, Kleinhenz K, Edwards EE, Gomez G, Hitchener G, Martins M, Kapczynski DR, Suarez DL, Alexander Morris ER, Hensley T, Beeby JS, Lejeune M, Swinford AK, Elvinger F, Dimitrov KM, Diel DG. (2024) Spillover of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus to dairy cattle. Nature. Jul 25.
- Harduin-Lepers, A. (2023) The vertebrate sialylation machinery: structure-function and molecular evolution of GT-29 sialyltransferases. Glycoconj J 40, 473–492.
February 2025, Janet Iwasa
http://doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2025_2


