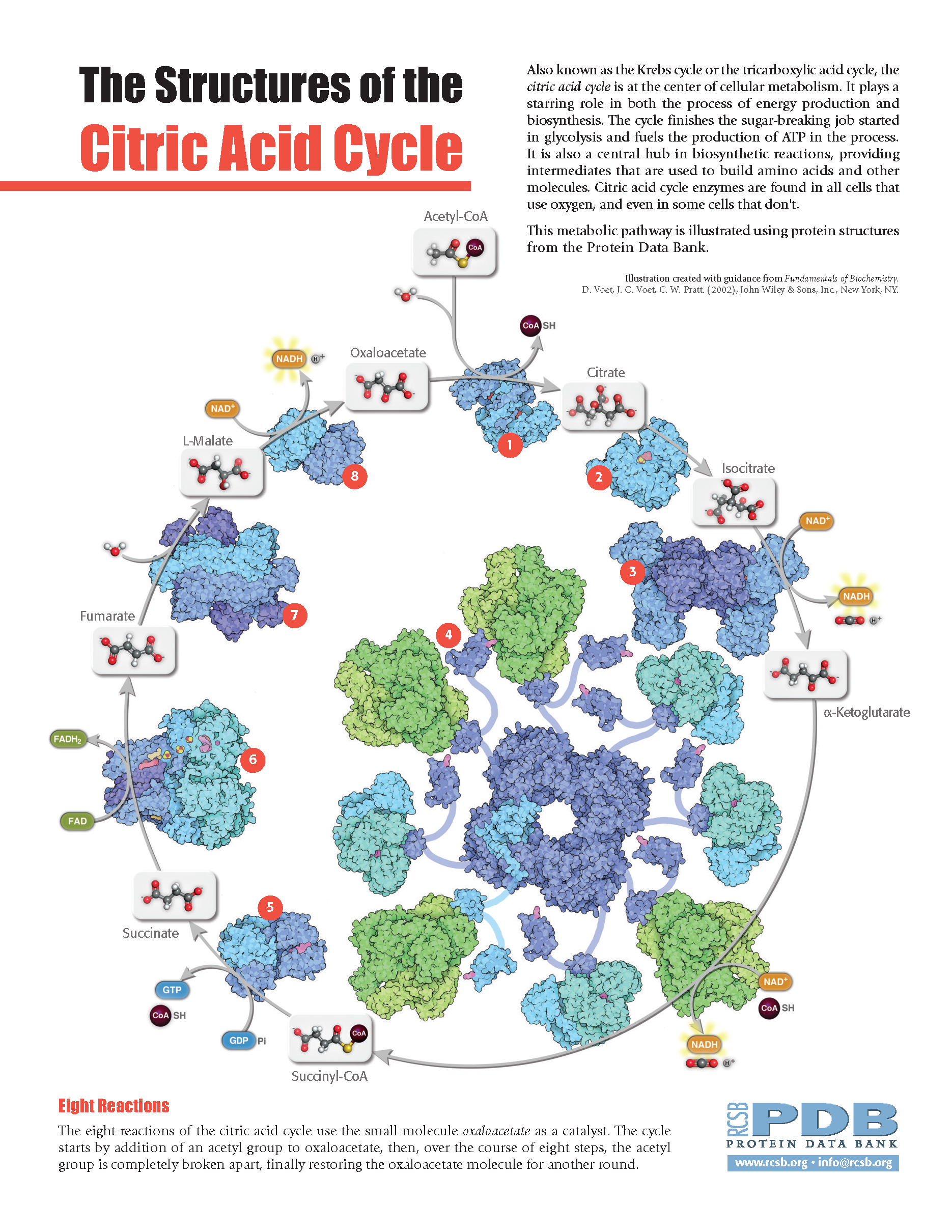
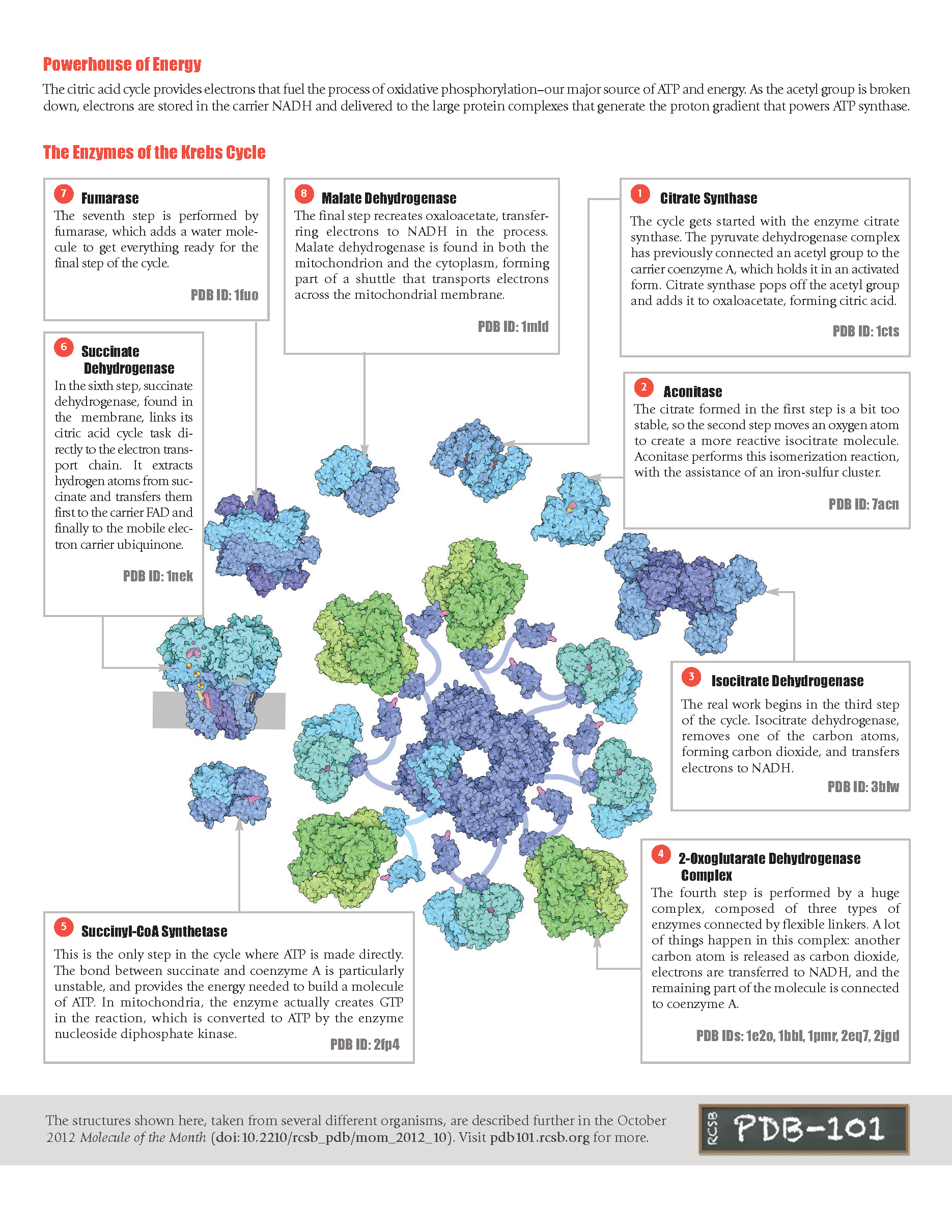
Structures of the Citric Acid Cycle
Also known as the Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle, the citric acid cycle is at the center of cellular metabolism. It plays a starring role in both the process of energy production and biosynthesis. The cycle finishes the sugar-breaking job started in glycolysis and fuels the production of ATP in the process. It is also a central hub in biosynthetic reactions, providing intermediates that are used to build amino acids and other molecules. Citric acid cycle enzymes are found in all cells that use oxygen, and even in some cells that don't. This metabolic pathway is illustrated using protein structures from the Protein Data Bank.