Molecular Models: Exploring the Structure of Fluorescent Proteins
- What is GFP? - An introduction to the molecule
- Build paper models of fluorescent proteins - Template and instructions for making the paper models of red and green fluorescent proteins
- Explore the atomic structure of GFP and compare it to that of DsRed - Interactive display of models
1. What is GFP?
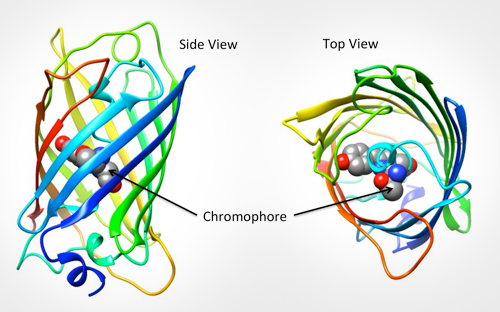
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) was first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria in the early 1960's. In the 1990's, methods were developed to express the GFP gene in worms and other organisms. The barrel-like structure of GFP was also determined in the 1990's. While there still is speculation about GFP's function in marine organisms, scientists have found a variety of uses for it in biology. For instance, as biological markers, GFP and other related fluorescent proteins provide an excellent way to track the location and expression of specific genes in cells or in an organism.
The specific part of the molecule responsible for GFPs fluorescence is called the chromophore. It is shown below left as grey, blue and red balls in the center of the barrel. The backbone atoms of three specific residues in GFP (Thr65-Tyr66-Gly67) make a special linkage to form a cyclic structure (shown on the bottom right). This cyclization is critical for the protein's ability to absorb blue light and fluoresce green.
To learn more, see the Molecule of the Month feature on GFP.
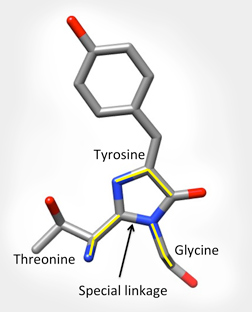
The Chromophore
2. Build Paper Models
Explore how the protein chain folds into its final 3D shape by building paper models of green and red fluorescent proteins.
3. Explore and Compare the Atomic Structure of GFP and GFP-related molecules
GFP is composed of a single protein chain. It is shown in the interactive Jmol in green as seen in the PDB entry 1ema. The GFP chromophore is shown using a green spacefill representation in the center of the protein.
A structurally similar protein from a type of coral is called Discosoma red (or DsRed) and fluoresces red. This protein naturally exists as a complex of four protein chains, each forming a beta barrel with a chromophore in the center as seen in PDB entry 1g7k. You can compare the structure of one of these chains to GFP to see striking similarity in shape, structure and chromophore location.
Although GFP and DsRed are distant relatives, key amino acids which are essential for cyclization (formation) of the respective chromophores are present at the exact same locations in both structures. The side chains of two such residues (Glutamate and Arginine) are shown pointing towards the chromophores in the cores of the barrel shaped proteins. Use the check box to toggle the display of these side chains.