Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Mycoplasma mycoides, 2011
Acknowledgement: Illustration by David S. Goodsell, The Scripps Research Institute. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-011
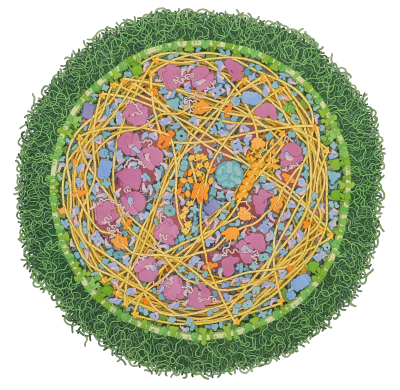
This illustration shows an entire mycoplasma cell, created in collaboration with Field Test Independent Film Corps. The cell shown here is about 300 nanometers in diameter, which is at the small end of the range of observed sizes.
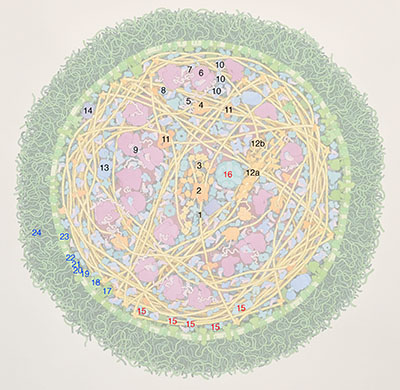
Key for “Mycoplasma mycoides”
-
Protein synthesis (labels in black)
- DNA
- DNA polymerase
- single-stranded-DNA binding protein (protects single-stranded portions during replication)
- RNA polymerase
- messenger RNA
- ribosome
- transfer RNA(in pink) and elongation factor Tu (in blue)
- elongation factor Tu and Ts
- elongation factor G
- aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
- topoisomerases
- Rec system for DNA repair: a) RecA, b) RecBC
- chaperonin GroEL (helps folding of new proteins)
- ClpA (destroys old proteins)
- glycolytic enymes
- pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- ATP synthase
- secretory proteins
- sodium pump
- zinc transporter
- magnesium transporter
- ABC transporter (different ABC transporters transport different types of molecules-ABC is short for "ATP-binding cassette")
- magnesium transporter
- lipoglycan (long carbohydrate chains connected to lipid in the membrane)
Enzymes for energy production (labels in red)
Membrane proteins (labels in blue)