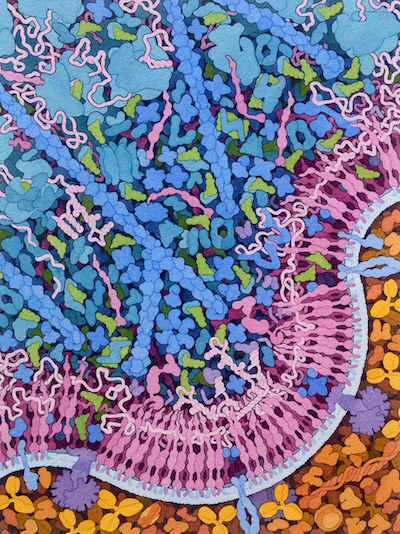
Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Transfer RNA and Gag Protein, 2021
Acknowledgement: Illustration by David S. Goodsell, Scripps Research and RCSB Protein Data Bank. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-037
This painting highlights work from the Center for HIV-1 RNA Studies (cRNA) and HIV Interactions in Viral Evolution Center (HIVE), showing that HIV-1 Gag polyprotein binds to tRNA and ribosomes, forming a reservoir of Gag molecules that are used during assembly and budding of new virions. The painting shows several steps in this process, starting with synthesis of Gag polyprotein (A) by ribosomes (B), and lipidation of the matrix domain of Gag by the cellular enzyme N-myristoyltransferase (C). Free Gag is associated with ribosomes (D) and tRNA (E), and ultimately interacts with the viral genomic RNA (F) and binds to the cell membrane, powering the budding of the virus from the cell surface.

This painting was created to accompany the report of the crystallographic structure of the matrix domain of Gag with tRNA (PDB ID 7mrl), published in Cell Host and Microbe. Information on the association of Gag with ribosomes is described in a publication in Journal of Molecular Biology. For more information on the other HIV and cellular molecules in the painting, please see Visualizations of HIV and HIV Life Cycle pages at the HIVE Center, and resources related to HIV and AIDS at PDB-101.