For each of the following questions select the best answer.
| 1. |
Biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids are primarily composed of
|
|
|
| 2. |
A hydrogen bonding interaction can be described as is
|
|
|
| 3. |
Protein building blocks are called
|
|
|
| 4. |
A peptide bond is formed as a result of a/an _____________ reaction between two amino acids?
|
|
|
| 5. |
When an enzyme changes its structure upon binding a substrate the following has changed:
|
|
|
| 6. |
The 3D structure of a protein can NOT be determined using which of the following methods
|
|
|
| 7. |
The ribbon diagram of a protein structure shows which of the following?
|
|
|
| 8. |
Which of the following resources is a primary resource for 3D structural data of biological macromolecules?
|
|
|
| 9. |
Visualization and analysis of a protein structure is NOT useful in
|
|
|
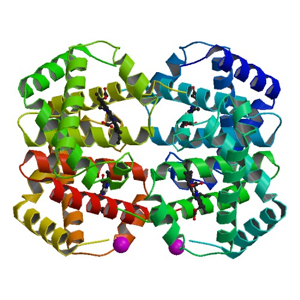
| 10. |
The structure shown below is that of
 |
|
|
| 11. |
Describe the main interactions (covalent and non-covalent) that help stabilize the 4 levels of protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures).
|
|
|
| 12. |
Describe two ways in which structures of a small globular protein and a DNA molecule are similar and two ways in which they are different.
|
|
|
| 13. |
Search the Protein Data Bank for the structure of human hemoglobin. Write down the PDB identifier, and entry title, of any one PDB entry from the ones that you find. Draw and save an image of this PDB entry in any visualization software of your choice, save the image and upload it here.
|
|
The following file types are accepted: ".doc", ".docx", ".ppt", ".pptx", ".pdf", ".gif", ".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png".
|