Caffeine and Adenosine: Antagonist and Agonist
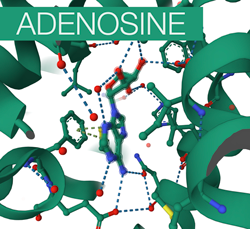
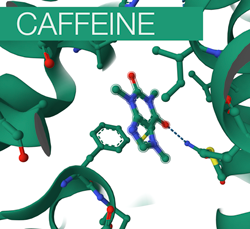
This short video uses the example of adenosine and caffeine to introduce two key concepts in pharmacology: the agonist and the antagonist. Both adenosine and caffeine bind to adenosine receptors located on neurons. Caffeine, the antagonist, blocks the receptor, while adenosine, the agonist, produces the biological response upon binding.
To learn more about this topic, explore the following resources:
Many drugs are agonists that bind to and activate targets; others are antagonists that bind to a target and prevent others from binding. To see an agonist and an antagonist drug in action, watch the PDB-101 video Opioids and Pain Signaling. The video details the action of morphine, an opioid receptor agonist, and naloxone, an opioid receptor antagonist. You can also learn how opioid drugs activate the G Protein to modulate the pain signal.
The G protein system is the most common method of signaling in our cells. Learn more from the Molecule of the Month on G Proteins
For an overview of how the neuronal signal is relayed in our bodies, watch the How Neurons Communicate video.