Molecule of the Month: Alpha-amylase
Amylases digest starch to produce glucose
Attacking Starch
Amylase in Action

Industrial Strength
Exploring the Structure
Amylase

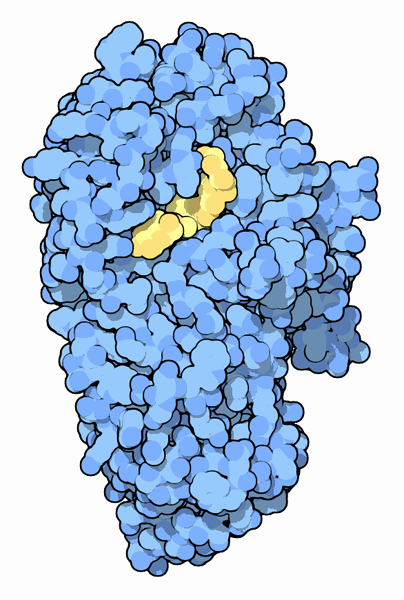
The active site of alpha-amylase contains a trio of acidic groups (colored white and red) that do most of the work. In the amylase shown here (PDB entry 1ppi ), glutamate 233, aspartate 197, and aspartate 300 work together to cleave the connection between two sugars in a starch chain. This structure contains a short chain of five sugar units (colored yellow and orange) bound in the active site. The site of cleavage is shown in blue. A calcium ion, shown as the large red sphere in the background, is found nearby where it stabilizes the structure of the enzyme. A chloride ion, shown as a green sphere, is bound underneath the active site in many amylases, where it may assist the reaction. Click on this image to explore the structure in an interactive JSmol.
Related PDB-101 Resources
- Browse Biological Energy
- Browse Enzymes
- Browse Biotechnology
References
- E. A. MacGregor, S. Janecek and B. Svensson (2001) Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the alpha-amylase family of enzymes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1546, 1-20.
- J. E. Nielsen and T. V. Borchert (2000) Protein engineering of bacterial alpha-amylases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1543, 253-274.
February 2006, David Goodsell
http://doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2006_2


