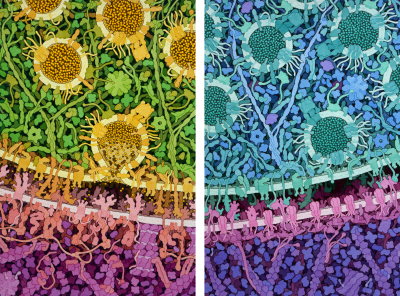
Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses, 2018
Acknowledgement: Illustration by David S. Goodsell. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-016
An excitatory synapse is shown on the left, with one synaptic vesicle releasing the neurotransmitter glutamate into the synapse, and an inhibitory synapse is shown on the right, with synaptic vesicles full of GABA. These illustrations were created for the exhibition “Brain – wider than the sky” at the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation in Lisbon, Portugal.
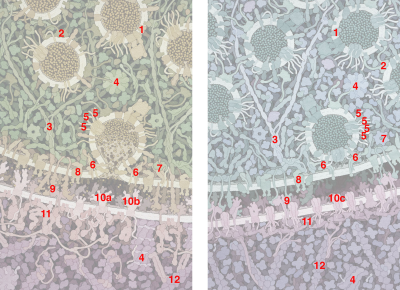
Key for "Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses"
- Transporters pump glutamate or GABA into vesicles.
- Synapsin holds vesicles in storage.
- Scaffolding proteins guide vesicles to the surface.
- CaMKII (Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II) regulates the action of many proteins.
- SNARE proteins will fuse vesicles with the membrane.
- SNARE complexes have docked the vesicle in the inhibitory painting, and fused the vesicle with the membrane in the excitatory painting.
- NSF protein separates the SNARE proteins after fusion.
- Voltage-dependent calcium channels trigger release of neurotransmitters.
- Neurexin and Neuroligin connect the two cells across the synapse.
- a. AMPAR (glutamate receptor), b. NMDAR (glutamate receptor), and c. GABA receptors bind to neurotransmitters and allow ions to enter the receiving cell.
- Postsynaptic density proteins form a scaffold to support the receiving cell.
- Actin filaments are part of the cytoskeleton.