Lipiarmycins
Discovery
In the 1970s lipiarmycins were derived from isolates of Actinoplanes deccanensis and Dactylosporangium aurantiacum, soil gram-positive bacteria of the actinomycetes family (Coronelli et al., 1975; Parenti et al., 1975; Sergio et al., 1975). Fidaxomicin (also known as lipiarmycin A3 or tiacumicin B) inhibits bacterial RNAP through a binding site and mechanism different from those of rifamycins (Hochlowski et al., 1987). Of the six different tiacumicin molecules isolated (A-F), tiacumicins B, C, and F had a strong activity against pathogens (McAlpine, 2017). Fidaxomicin (formerly known as lipiarmycin A3 or tiacumicin B) was isolated as an antibiotic that mediated by inhibition of a site in the bacterial RNA polymerase, distinct from where rifamycins interact (Srivastava et al., 2011; Venugopal and Johnson, 2012; Boyaci et al., 2018).
Overview of Chemistry
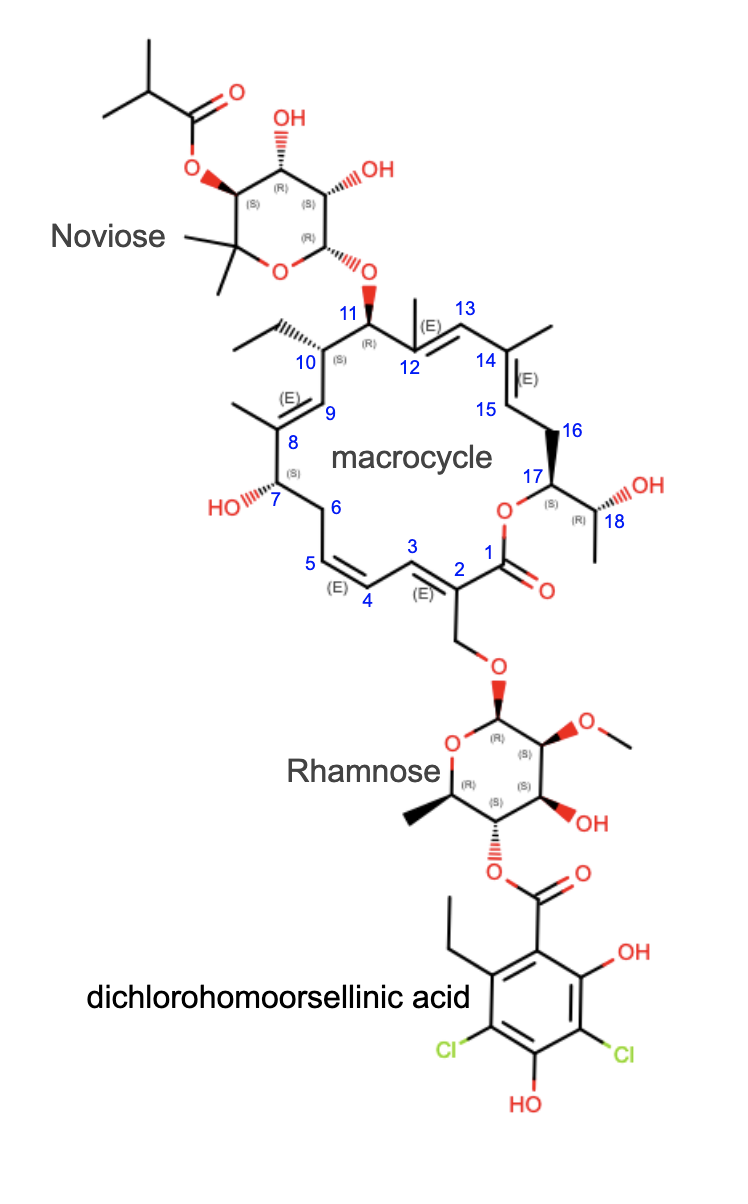
Lipiarmycin antibiotics contain an 18-membered macrolactone ring and target bacterial RNA polymerases. In fidaxomycin, a member of this antibiotic class, the macrocycle is glycated on either side with noviose and rhamnose, and the latter is esterified to a dichlorohomoorsellinic acid subunit (Figure 1).
Note that other macrocyclic antibiotics (e.g., 14-membered erythromycin and clarithromycin or 15-membered azithromycin), bind to the ribosome.
Resistance
The predominant mechanism of resistance to lipiarmycins is drug target (i.e., RNA polymerase β and β' subunits, RpoB and RpoC) modification by mutation.
Learn more about fidoxamicin resistance.
References
Boyaci, H., Chen, J., Lilic, M., Palka, M., Mooney, R. A., Landick, R., Darst, S. A., Campbell, E. A. (2018). Fidaxomicin jams Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNA polymerase motions needed for initiation via RbpA contacts. eLife, 7, e34823. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.34823
Coronelli, C., White, R. J., Lancini, G. C., Parenti, F. (1975) Lipiarmycin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes. II. Isolation, chemical, biological and biochemical characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 28(4):253-9. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.28.253
Hochlowski, J. E., Swanson, S. J., Ranfranz, L. M., Whittern, D. N., Buko, A. M., McAlpine, J. B. (1987) Tiacumicins, a novel complex of 18-membered macrolides. II. Isolation and structure determination. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 40(5):575-88. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.40.575
Lin, W., Das, K., Degen, D., Mazumder, A., Duchi, D., Wang, D., Ebright, Y.W., Ebright, R.Y., Sineva, E., Gigliotti, M., Srivastava, A., Mandal, S., Jiang, Y., Liu, Y., Yin, R., Zhang, Z., Eng, E.T., Thomas, D., Donadio, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, C., Kapanidis, A.N., Ebright, R.H. (2018) Structural Basis of Transcription Inhibition by Fidaxomicin (Lipiarmycin A3). Mol Cell. 70(1):60-71.e15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.02.026
McAlpine, J. B. (2017) The ups and downs of drug discovery: the early history of Fidaxomicin. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 70(5):492-494. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.157
Parenti, F., Pagani, H., Beretta, G. (1975) Lipiarmycin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes. I. Description of the producer strain and fermentation studies. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 28(4):247-52. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.28.247
Sergio, S., Pirali, G., White, R., Parenti, F. (1975) Lipiarmycin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes III. Mechanism of action. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 28(7):543-9. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.28.543
Srivastava, A., Talaue, M., Liu, S., Degen, D., Ebright, R. Y., Sineva, E., Chakraborty, A., Druzhinin, S. Y., Chatterjee, S., Mukhopadhyay, J., Ebright, Y. W., Zozula, A., Shen, J., Sengupta, S., Niedfeldt, R. R., Xin, C., Kaneko, T., Irschik, H., Jansen, R., Donadio, S., Connell, N., Ebright, R. H. (2011). New target for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase: 'switch region'. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 14(5), 532-543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2011.07.030
Venugopal, A. A., Johnson, S. (2012) Fidaxomicin: A Novel Macrocyclic Antibiotic Approved for Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection, Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 54, Issue 4, Pages 568–574, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cir830
March 2025, Shuchismita Dutta; Reviewed by Dr. Richard Ebright
https://doi.org/10.2210/rcsb_pdb/GH/AMR/drugs/antibiotics/rna-synth/rp/lipiarmycin