Immune System
our protection from infection
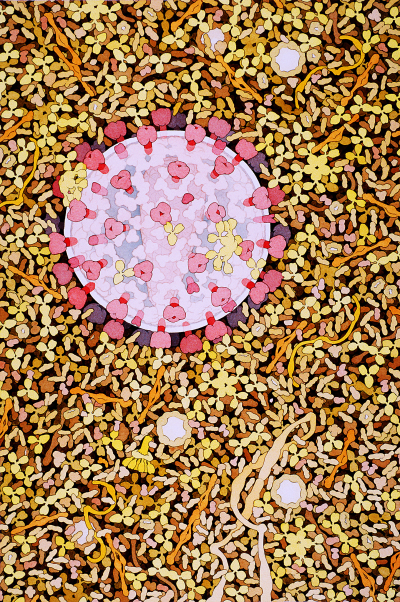
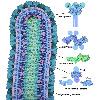
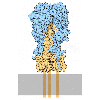
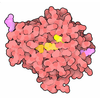
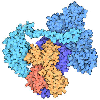
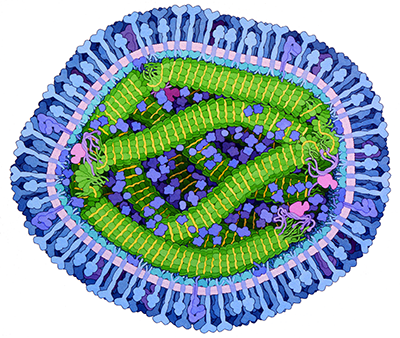
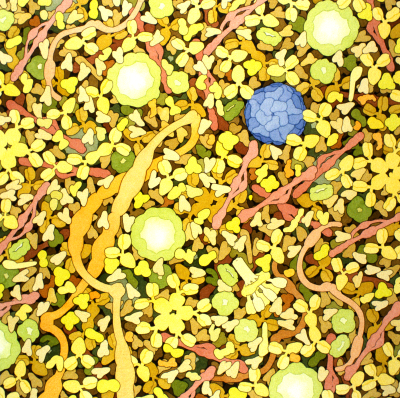
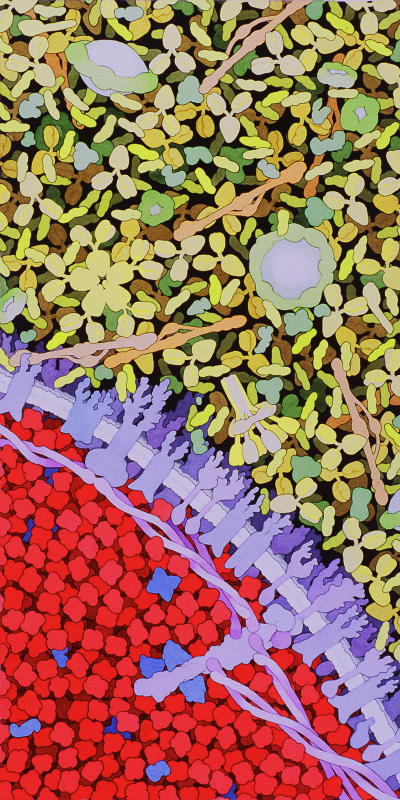
The bloodstream is filled with molecules and cells that search for invaders and destroy them if they are found. Atomic structures have revealed how the immune system recognizes viruses and bacteria while leaving our normal molecules alone. Knowledge of the immune system and its targets is allowing medical science to develop powerful new treatments to fight disease.